Global WLAN industry development has already experienced new shipment highs inspired by the retail market take-off and notebook PC adoption of built-in modules. In 2005 the industry will enter the applications diversification and expansion stage. Taiwanese makers at the end of 2004 won large orders for PSP WLAN applications, expanding their business from the PC and broadband segments. Products exhibited at CES 2005 include audio-video and voice applications, driving the inclusion of home WLAN into triple play applications.
|
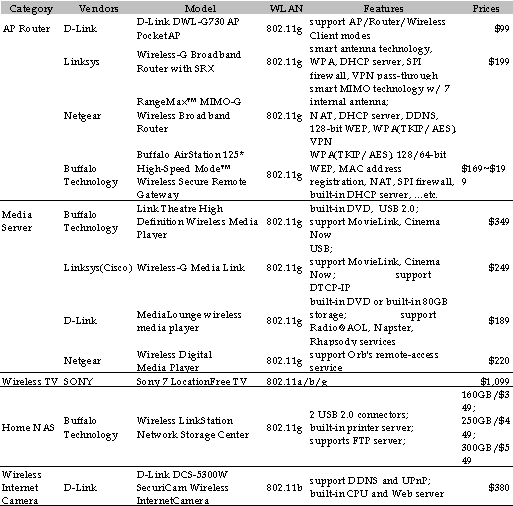
Figure 19 WLAN LAN Offerings Displayed at CES 2005 |
|
|
|
Source: MIC, March 2005 |
In 2005 WLAN will continue to expand to AP router. Many brand-name makers have rolled out MIMO technology pre-n products. In addition to transmission rates in excess of 100Mpbs, transmission distances are great enough that home wireless transmission coverage will not have any dead zones.
2005 WLAN media server/client products will continue to upgrade transmission specifications. Across-the-board upgrade from 802.11b to 802.11g to support images, audio, and video sharing will be complemented by transmission quality assurance and partial support for 802.11e. The home audio and video equipment digitalization trend has taken off, and internal WLAN LCD TV and DVD player interface products are being rolled out. With the global digital TV trend, as well as the multi-room viewing habits growing more common, demand for the aforementioned WLAN products should begin warming up in 2005. As home networks become more widespread, many makers expect demand for home network storage to pick up, and are rolling out home network storage centers for multimedia file transmission and home office transmission.
Finally, between 2004 and 2005 MSOs (Multiple Systems Operator), telecoms, and ITSP (Internet Telephony Service Providers) have already begun, or will begin, offering VoIP services. Global VoIP user numbers should exhibit strong growth. From the standpoint of service providers, home broadband equipment is already seeing an increasing trend to shift to wireless. As a result, future diversification of service demand will in all probability result in VoIP phones adopting wireless specifications. VoIP Wi-Fi phone, previously targeted mainly at vertical markets, will thus shift toward home applications markets, driving WLAN expansion into voice applications and related products.
Appendix
Research Scope
Taiwanese WLAN shipments encompass all WLAN NIC, modules, and access points produced by Taiwanese makers anywhere in the world.
Definitions
Business Types
OEM
The OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) business model entails carrying out product manufacturing or assembly according to specifications supplied by the customer. The OEM business model emphasizes production efficiency; thus, in order to lower costs, customers outsource manufacturing to OEM providers. This cooperation forms a division of labor among design, manufacturing, and sales.
ODM
The ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) business model entails undertaking product design and manufacturing, but not direct retail sales or brand promotion. ODM providers either collaborate with customers on product specifications or independently design products according to customer specifications; the ODM provider then receives manufacturing orders upon customer approval. The ODM model links the sales capabilities of the ODM customer and the design and manufacturing capabilities of the ODM provider, developing a cooperative division of labor throughout the product's value chain.
Product Types
WLAN NIC
WLAN function as a data communications system that provides wireless peer-to-peer and point-to-point connectivity, usually within a building. In place of twisted-pair or coaxial wires or optical fiber used in LANs, WLAN transmit and receive data over electromagnetic waves over ISM (Industry, Scientific, Medical) bands between 2.4GHz or 5.8GHz.
WLAN NIC refers to a PCB (Printed Circuit Board) that is attached or embedded into a PC or mobile device. A WLAN NIC provides device to device or device to WLAN AP data communications on a specific frequency or radio band.
WLAN AP
A WLAN AP connects a wired LAN to one or many WLAN devices, or acts as a bridge between two WLAN devices. Wireless Access points typically incorporate an Ethernet port and radio communications capability.
Routers
Routers control network flow by determining the best routing for data transmission between a transmitter and a receiver. Routers are typically controlled by software and are programmed to provide the most inexpensive, fastest, or least busy of all available routes. Routers operate at layer 3 of the ISO-OSI (International Standard Organization's Open System Interconnect) model. Routers can be further divided by the number and type of network protocols they can support and by the number of ports available for protocol routing.
Glossary of Terms
|
ADSL |
|
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line |
|
|
AP |
|
Access Point |
|
|
ASP |
|
Average Sell Price |
|
|
CE |
|
Consumer Electronics |
|
|
CES |
|
Consumer Electronics Association |
|
|
CF |
|
Compact Flash |
|
CPE |
|
Customer Premises Equipment |
|
|
CPU |
|
Central Processing Unit |
|
|
ITSP |
|
Internet Telephony Service Providers |
|
|
MIMO |
|
Multiple-input ,Multiple-output |
|
|
MSO |
|
Multiple System Operator |
|
|
MSO |
|
Multiple Systems Operator |
|
|
NIC |
|
Network Interface Card |
|
|
PSP |
|
PlayStation Portable |
|
|
RF |
|
Radio Frequency |
|
|
VoIP |
|
Voice-over-Internet Protocol |
|
|
WLAN |
|
Wireless Local Area Network |