3D Monitor Market Emerging Strongly
In order to effectively stimulate growth in the monitor market, monitor vendors have been aggressively trying to expand emerging application markets in recent years. The aim of their efforts is to extend the market for monitors from the enterprise segment to the entertainment segment. They have focused on 3D monitors for the gaming segment and have conducted relevant technology development.
3D displays, the most important element of 3D monitors, have started to feel the impact of end-market demand. The share of monitors among 3D display applications at SID 2009 already reached 20.0%.
All 3D monitors showcased at SID 2009 featured special glasses technology, including polarizer-type glasses technology and shutter-type glasses technology. The parallax element technology involved in 3D displays with special glasses is relatively mature, and the supply chain is able to ship products rapidly in order to meet demand in the emerging 3D monitor market. Therefore, the share of 3D displays featuring special 3D glasses increased considerably at SID 2009.
LG Display Has Technology Lead in Lenticular Lens Technology; Other Vendors Developing New Technologies
Regarding prior art technology for lenticular lens, yield rates of processes within the lens were difficult to control and costs were high. Furthermore, lenticular lens technology patents are controlled by Philips of the Netherlands. Due to technology bottlenecks in production processes and technology patent barriers, other companies reduced their aggressiveness in terms of investments for lenticular lens technology development.
By using new technologies developed by Philips, LG Display has achieved breakthroughs in lenticular lens production technologies. The company has conducted successful production trials for a flat-panel GRIN lenticular lens 2D/3D switchable display product, and it has thoroughly solved yield rate problems of previous technologies.
Due to this breakthrough, LG display has increased its technology lead in lenticular lens technology. As a result, other companies want to avoid LG Display in the lenticular lens arena and are developing new types of parallax element technology, including: barrier lens, dual-depth imaging switchable, time sequential OCB technology etc.
After examining products adopting these new technologies, it was found that the 3D effects of these products can not yet compete with the mainstream lenticular lens technology. Drawbacks of these new technologies include: small viewing angle, low brightness, flicker, crosstalk etc.
Lenticular lens technology has thus achieved a high level in terms of 3D visual effects, while LG Display has achieved breakthroughs in terms of production processes, which were previously hampered by low yield rates. Therefore, MIC forecasts that in the coming few years lenticular lens technology will continue to be the mainstream technology for 3D displays.
Appendix
Research Scope
This report analyzes 3D display products showcased at the SID Display Week 2009, held in the US city of San Antonio at the Henry B. Gonzalez Convention Center from May 31 to June 5. This analysis sheds more light on technology and product development 3D displays.
Technology Summary
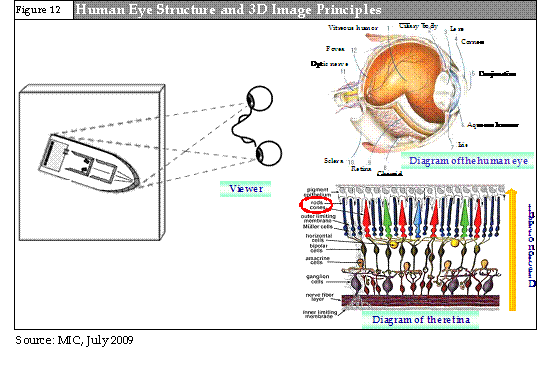
As there is a distance of approximately 6.5 cm between the left eye and right eye, the visual data received by the two eye retinas differs slightly due to differences in viewing angle. There are specific cells in the retina which are responsible for visual signals, including rods and cones. These are responsible for transforming light brightness and colors into optic nerve signals. The brain combines the two different viewing angle data to create a sense of depth. This leads to 3D visual effects for human eyes.
Real 3D visual effects are created through two types of parallax effects: binocular parallax and motion parallax. Binocular parallax functions as described above: different viewing angles of the right eye and left eye lead to different visual information received by the two eyes. These two sources of visual information are combined in the brain to form 3D effects. As for motion parallax, due to viewing angle changes as a result of motion, the received visual content is also constantly changing. The two sources of information are also combined by the brain and made into 3D visual effects.
By using either one of these two parallax effects, human eyes can experience 3D when viewing objects. If a 3D display features the two types of parallax effects, this can be defined as autostereoscopic display.
Therefore, if companies aim to create 3D visual effects for flat-panel displays, through parallax element technology each pixel on the display can be enabled to operate through parallax elements, and be able to modulate light brightness, colors and direction. This can enable the image data received by the left eye and right eye to form 3D effects due to viewing angle differences. The modulation of brightness and colors can determine the color resolution of a display. The direction of lights can determine the viewing zone space resolution.
Regarding flat-panel 3D displays with parallax technology, the strength of its display features relies on display pixels' modulation capabilities for brightness, colors and directions.
Glossary of Terms
|
TFT-LCD |
|
Thin Film Transistor Liquid Crystal Display |
|
a-Si TFT-LCD |
|
Amorphous Silicon Thin Film Transistor LCD |
|
LTPS TFT-LCD |
|
Low Temperature Poly-Silicon Thin Film Transistor LCD |
|
OLED |
|
Organic Light Emitting Diode |
|
AM-OLED |
|
Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode |
|
PM-OLED |
|
Passive Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode |
|
E-Paper |
|
Electronic-Paper |
|
OCB |
|
Optically Compensated Bend |
|
MEMS |
|
Microelectro Mechanical System |
|
GRIN |
|
Gradient Index |
|
FPD |
|
Flat Panel Display |
List of Companies
|
LG Display |
|
|
|
NEC LCD |
|
|
|
Philips |
|
|
|
Samsung |
|
|
|
Sharp |
|
|
|
TMD |
|
|
|
Wintek |
|
|