Though Laggard in Commercialization Schedule, LTE Is Expected to Benefit from Strong Industry Support
Considering industry chain support, overall development of various regions, telecom operators' network upgrade strategies, available spectrums, and application services, it is projected that LTE will not make instant impact on the mobile communications market upon launch. However, due to the scale and comprehensiveness of the mobile communications industry supply chain, various major players, ranging from component makers to equipment vendors, have actively engaged in pushing the interoperability and testing of LTE software and hardware. Should LTE standard be announced, it is expected that telecom operators will be able to launch commercial LTE services in a relatively short period of time with the support from the industry supply chain
In contrast, WiMAX has the head start over LTE as WiMAX is already quite advanced in the progress of standardization. Moreover, many emerging markets have opted for WiMAX for the deployment of broadband communications network, as WiMAX boasts less expensive construction costs. In spite of the belatedness in commercialization, LTE is likely to catch up with WiMAX and continue the leading status of the 3GGP group in the market thanks to said support from the industry chain as well as plenty of available spectrum bands.
|
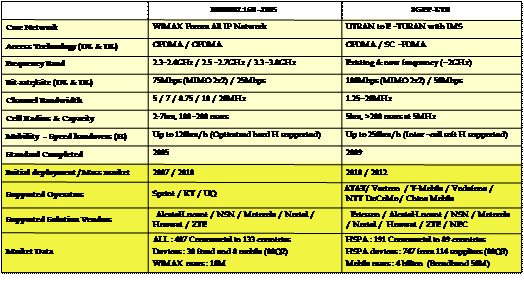
Figure 7 |
WiMAX vs. LTE |
|
|
|
Source: Motorola, Ericsson, WiMAX Forum, compiled by MIC, February 2009 |
ARPU Growth Enabled by High-speed Networks Expected to Play an Important Role in Operators' Willingness to Adopt LTE
Although LTE is the future trend of the current 3G mobile communications industry, some important issues are expected to affect operators' LTE deployment progress in the next two to three years. For most mobile operators, the problem does not lie in the amount of capital spending required for LTE network deployment but in whether the business models enabled by LTE will serve to bridge the gap between current network data capacity and growing data service demand. Therefore, LTE forerunners' capability of establishing ideal data service content and prices will be an important point of reference for the followers.
As regards technology and cost, the industry is generally of the opinion that the success of LTE will depend on whether the prices of equipment will be able to lower the costs per Mbps, or operators' willingness to adopt LTE will be affected. The scale of capital investments in LTE deployment can be reduced by using the existing 3G base stations, sharing networks, and upgrading the backhaul. Moreover, LTE supports self-organization and self-optimization, enabling the upgrade of hardware by means of software, thereby cutting back on network management and maintenance costs. In indoor environments, wireless signal coverage and transmission can be enhanced with the support of femtocells, so as to ensure the quality of service. In addition, deployment of the LTE network can coexist with the existing 2G/3G networks, and the utilization of hotspots, coupled with multi-mode access devices, to provide high-speed Internet services in the initial phase of network deployment is also a feasible operating model. Still, said options all rest on individual operators' own discretion.
The Number of LTE Subscribers to See Substantial Growth Starting in 2012
Owing to the continuing growth of the 3G industry clusters and mobile data usage, it is forecasted that mobile data usage volume will grow over 10 times in comparison with 2008, reaching a subscriber base of approximately 1.95 billion. In the meantime, telecom carriers will have to keep upgrading their mobile broadband networks in order to meet market demand. There are several large mobile service operators in North America, Western Europe and East Asia prepared to launch LTE trial services in 2009. Nevertheless, the full-scale commercialization of LTE still awaits more definite development of spectrum utilization, license issuance, standard formulation, software/hardware technologies, and trials, as well as more active deployment by other industry value chain players. As for the timing for LTE takeoff, whether telecom carriers will have to pass through the stage of HSPA+ to LTE is expected to be an important issue in the mobile communications industry in 2009. It is expected that following one or two years of network trials as well as establishment of terminal access devices and business models, the number of LTE subscribers will see substantial growth starting in 2012.
Appendix
Glossary of Terms
|
ARIB |
|
Association of Radio Industries and Businesses |
|
ATIS |
|
Alliance for Telecommunications Industry Solutions |
|
ATM |
|
Asynchronous Transfer Mode |
|
BSR |
|
Base Station Router |
|
BTS |
|
Base Transceiver Station |
|
CCSA |
|
China Communications Standards Association |
|
CPC |
|
Continuous Packet Connectivity |
|
eNodeB |
|
Evolved NodeB |
|
EPC |
|
Evolved Packet Core |
|
EPS |
|
Evolved Packet System |
|
ETSI |
|
European Telecommunications Standards Institute |
|
FMC |
|
Fixed Mobile Convergence |
|
FTP |
|
File Transfer Protocol |
|
GSM |
|
Global System for Mobile Communications |
|
HSPA |
|
High Speed Packet Access |
|
IMS |
|
IP Multimedia Subsystem |
|
IMT |
|
International Mobile Telecommunications |
|
IP |
|
Internet Protocol |
|
LSTI |
|
LTE/SAE Trial Initiative |
|
LTE |
|
Long Term Evolution |
|
MBMS |
|
Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Service |
|
MIMO |
|
Multiple Input Multiple Output |
|
MWC |
|
Mobile World Congress |
|
NGMN |
|
Next Generation Mobile Networks |
|
OFDM |
|
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplex |
|
OFDMA |
|
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access |
|
RAN |
|
Radio Access Network |
|
RF |
|
Radio Frequency |
|
TTA |
|
Telecommunications Technology Association |
|
TTC |
|
Telecommunication Technology Committee |
|
UMB |
|
Ultra Mobile Broadband |
|
UMTS |
|
Universal Mobile Telecommunications System |
|
WCDMA |
|
Wideband Code Division Multiple Access |
|
3GPP |
|
3rd Generation Partnership Project |
List of Companies
|
Alcatel-Lucent |
|
|
|
Bell Labs |
|
|
|
Broadcom |
|
|
|
Ericsson |
|
|
|
Freescale |
|
|
|
Fujitsu |
|
|
|
Huawei |
|
華為 |
|
Infineon |
|
|
|
LG |
|
|
|
Motorola |
|
|
|
NEC |
|
|
|
Nokia |
|
|
|
Nokia Siemens Networks |
|
|
|
Nortel |
|
|
|
NTT DoCoMo |
|
|
|
NXP |
|
|
|
Qualcomm |
|
|
|
Samsung |
|
|
|
Sony Ericsson |
|
|
|
STMicroelectronics |
|
|
|
T-Mobile |
|
|
|
Verizon |
|
|
|
Vodafone |