MIC Perspective
New Smart Handheld Devices Emerge, IC Market Structure Projected to Change
Smart handheld devices traditionally refer to Smartphones. Market share structure of Smartphones has been stable, and since Smartphones are usually equipped with 3G/3.5G communication technology, Qualcomm is currently the market leader because the company owns a majority of 3G/3.5G technology patents. With the emergence of other types of products with new specifications, such as tablet devices, 3G/3.5G communication function becomes unnecessary for some devices and AP performance becomes more important. Conventional major processor chip suppliers seek to foray into the total solution market by acquiring baseband businesses from other companies. While some branded vendors began to develop chips on their own aiming to optimize product performance. It is observed that the above-mentioned business model is similar to that of Nokia and Motorola whose businesses originally covered from chipset design to end-market product manufacturing.
As regards the transition to 4G from 3G/3.5G communication technology, since no company owns a majority of LTE patents, Qualcomm, therefore, is projected to meet challenges when attempting to secure its position in the LTE solution market. Nokia, Samsung, LG, and Huawei are able to launch product development on their own or team up with other vendors. With their advantages in the end-market product segments, these companies are likely to carve out a share of the LTE solution market.
|
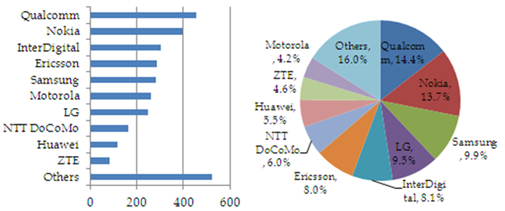
Figure 9
|
Total LTE Patents and Pending Patents
|
|
|
|
Note: The numbers of patents calculated include patents filed with ETSI as of September 30, 2011. Picture on the left illustrates total patents and pending patents. Picture on the right represents ratio of highest essentiality to LTE standards.
Source: Article One Partner & Thomson Reuters, February 2012, compiled by MIC, May 2012
|
| |
|
Looking at technology development blueprint of major chip suppliers, it can be seen that Nvidia is projected to release Grey integrating between Icera 500 LTE modem and Tegra 3 solution. Intel Mobile is anticipated to unveil solutions integrating LTE baseband chips at the end of 2012. In other words, instead of the traditional mobile communications chip suppliers such as ST-Ericsson and TI, Qualcomm now has to compete with Nvidia and Intel, which have dominated the PC market for a long period of time. With its advanced semiconductor process at 32nm and smaller architecture, if Intel is able to lower power consumption and increase performance/price value in a short period of time, the company is likely to make breakthrough as chip designers are projected to see insufficient manufacturing capacities provided by semiconductor foundries during the period from 2012 to 2013.
High-end IC Market to See Intensified Competition, Entry-level IC Market to Witness Further Development
Competition in the high-end, mid-range, and entry-level IC markets is projected to be different. In the high-end IC market, product performance and consistent power consumption are crucial. It is thus can be seen that most of the branded vendors place orders with major international chip suppliers, especially those running large-scale business operations and having the capabilities to continuously conduct R&D and ensure foundry capacity, such as Qualcomm, Samsung, Nvidia, Intel, and ST-Ericsson. Barrier to market entry in this segment is relatively high. Besides, high-end models are usually equipped with 4G support, such as LTE, but if single LTE baseband is used with single AP, insufficient space problem resulted from circuit design will be encountered. Therefore, integrated system on a chip becomes the mainstream and chip suppliers thus need to be equipped with LTE baseband technology in order to compete. TI and Marvell which have relatively less LTE technology capabilities are projected to see tough challenges.
In the mid-range chip market, since Qualcomm has considerable 3G technology patents, provides integrated solutions, and delivers high performance/price value, it is projected that Qualcomm will continue its dominance in the market. As regards ST-Ericsson which is more likely to compete head-to-head with Qualcomm compared to other suppliers, has been facing operating losses in recent years, and the company failed to successfully challenge Qualcomm's dominance as a result. Will ST-Ericsson be able to release products with high performance/price value after business restructuring and maintain good relations with Nokia, Samsung, and Sony Ericsson remain to be seen.
Diversified mobile phone manufacturing and sales systems in the emerging countries have stimulated competition among various chip suppliers in the entry-level IC market. Qualcomm is able to secure its dominance leveraging its in-depth cooperative ties with major branded vendors. Branded vendors, however, usually have less interest in providing Smartphones priced below 1000 RMB (US$156.3; US$1 = 6.4 RMB) which bring in less profit, and major telecom operators have less confident in product performance of such devices, either. Nevertheless, such Smartphones are appealing to consumers with relatively low incomes, and buying and selling of such Smartphones are often take place at retail channel. Major chip suppliers such as Qualcomm are projected to generate less profit in the emerging markets, and will the major suppliers aggressively cultivate these markets and deploy technical support services remain to be seen. MediaTek, Spreadtrum, and Mstar have built strong business ties with Chinese second-tier vendors and white brand vendors and enjoyed rapid market volume increase, and it is thus projected that these suppliers will continue to see growth compared to chip suppliers focusing on high-end chip market.
Taiwanese IC Designers Expected to See Growth, System Integrators to Encounter Challenges
It is projected that performance growth of high-end ICs will be limited not because chip design will see technology bottleneck, but rather because the development of peripheral components, such as memory read/write speed, panel specifications, and battery run time, fail to catch up. Thanks to reference design, entry-level ICs are expected to see further development, and entry-level models will thus enjoy stronger growth momentum compared to high-end models.
Taiwanese IC designers' advantages lie in providing products with high performance/price value with relatively low costs. As MediaTek, Qualcomm, and Spreadtrum have aggressively released reference design solutions, Taiwanese chip designers are expected to gain certification and even get involved in reference design leveraging their R&D capabilities. The rapid development of reference design solution market is anticipated to boost growth of Taiwanese chip designers. Nevertheless, the Chinese chip designers have posed threats on the Taiwanese counterparts since some customers have relatively low loyalty and focus mainly on costs. Understanding diversified demand in the emerging markets is thus projected to be the key.
Taiwanese system integrators are projected to meet considerable challenges. As per the development of Smartphones, market shares of Taiwanese integrators' major clients, such as Nokia, Motorola, and Sony Ericsson, began to decrease. Emerging vendors such as Samsung and Apple prefer to conduct IC design and product R&D on their own and place no orders with Taiwanese ODM (Original Design Manufacturing) makers. Furthermore, as MediaTek and other vendors have released mature reference design solutions, Taiwanese ODM makers thus began to lose their advantages as regards platform introduction and design. Some of them are even replaced by IDHs (Independent Design Houses) from China.
Under such backdrop, as product differentiation can only be generated by different hardware specifications, such as panels and cameras, it is projected that system integrators will strengthen their strategic alliances with upstream key component makers so as to ensure stable supply of high-end components and stand out in competition.
Appendix
Glossary of Terms
|
AP
|
|
Application Processor
|
|
ASP
|
|
Average Selling Price
|
|
CAGR
|
|
Compound Annual Growth Rate
|
|
CDMA
|
|
Code Division Multiple Access
|
|
EDGE
|
|
Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution
|
|
EV-DO
|
|
Evolution Data Only
|
|
GPRS
|
|
General Packet Radio Service
|
|
GPU
|
|
Graphic Processing Unit
|
|
GSM
|
|
Global System for Mobile Communications
|
|
HSPA
|
|
High Speed Packet Access
|
|
IDH
|
|
Independent Design House
|
|
LTE
|
|
Long Term Evolution
|
|
MSM
|
|
Mobile Station Modem
|
|
ODM
|
|
Original Design Manufacturing
|
|
OS
|
|
Operating System
|
|
PCB
|
|
Printed Circuit Board
|
|
PCBA
|
|
Printed Circuit Board Assembly
|
|
QRD
|
|
Qualcomm Reference Design
|
|
RAM
|
|
Random Access Memory
|
|
RF
|
|
Radio Frequency
|
|
SIM
|
|
Subscriber Identity Module
|
|
SIP
|
|
Silicon Intellectual Property
|
|
SoC
|
|
System on Chip
|
|
TD-SCDMA
|
|
Time Division-Synchronous Code Division Multiple Access
|
|
UI
|
|
User Interface
|
|
VoLTE
|
|
Voice over LTE
|
|
WCDMA
|
|
Wideband Code Division Multiple Access
|
List of Companies
|
Acer
|
|
宏碁
|
|
Amazon
|
|
|
|
Apple
|
|
|
|
Asus
|
|
華碩
|
|
AT&T
|
|
|
|
Barnes & Noble
|
|
|
|
CoolPAD
|
|
|
|
Ericsson
|
|
|
|
ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute)
|
|
|
|
Google
|
|
|
|
GSA (The Global mobile Suppliers Association)
|
|
|
|
Hisense
|
|
|
|
HTC
|
|
宏達電
|
|
Huawei
|
|
|
|
Infineon
|
|
|
|
Intel
|
|
|
|
Intel Mobile
|
|
|
|
InterDigital
|
|
|
|
Leadcore
|
|
|
|
Lenovo
|
|
|
|
LG
|
|
|
|
Marvell
|
|
|
|
MediaTek
|
|
聯發科
|
|
Motorola
|
|
|
|
Mstar
|
|
晨星
|
|
Nokia
|
|
|
|
NTT Docomo
|
|
|
|
Nvidia
|
|
|
|
Qualcomm
|
|
|
|
RIM
|
|
|
|
Samsung
|
|
|
|
Sharp
|
|
|
|
Sony Ericsson
|
|
|
|
Spreadtrum
|
|
|
|
ST-Ericsson
|
|
|
|
STMicroelectronics
|
|
|
|
The Research Institution of China Mobile
|
|
|
|
TI
|
|
|
|
Verizon
|
|
|
|
ZTE
|
|
|